Business Process Automation Through Advanced ERP: Complete Guide, Features and Details
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, staying competitive requires more than just hard work; it demands efficiency, agility, and informed decision-making. For years, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have been the backbone of many organizations, integrating various departments and streamlining operations. However, the ERP of yesterday is not the ERP of today. Advanced ERP solutions are now leveraging technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to offer a level of business process automation previously unimaginable. This isn’t just about automating repetitive tasks; it’s about fundamentally transforming how businesses operate.
As someone who has been deeply involved in ERP implementations and optimization projects for over a decade, I’ve witnessed firsthand the transformative power of advanced ERP systems. I’ve also seen the challenges organizations face when adopting these complex solutions. The journey from initial assessment to successful implementation is often fraught with obstacles, from selecting the right vendor to ensuring user adoption. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to business process automation through advanced ERP, covering key features, implementation strategies, and practical insights to help you navigate this complex landscape.

This guide is designed to be your go-to resource for understanding how advanced ERP can automate your business processes, improve efficiency, and drive growth. We’ll explore the core features of advanced ERP, discuss the benefits of automation, delve into the implementation process, and address common pain points. Whether you’re a seasoned executive looking to upgrade your existing ERP system or a business owner considering ERP for the first time, this article will equip you with the knowledge and insights you need to make informed decisions and achieve lasting success.
What is Advanced ERP and Why is Automation Crucial?
Advanced ERP systems represent the evolution of traditional ERP, incorporating cutting-edge technologies to enhance their capabilities. They move beyond simply integrating departments and managing data to actively automating processes, predicting trends, and providing real-time insights. This shift is driven by the need for businesses to be more agile, responsive, and data-driven in today’s competitive environment.
Key Differences Between Traditional and Advanced ERP
While traditional ERP systems primarily focus on data management and process integration, advanced ERP systems take it a step further with the following key differences:
- AI and ML Integration: Advanced ERP utilizes AI and ML algorithms to automate tasks, predict future trends, and optimize decision-making.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): RPA bots automate repetitive, rule-based tasks, freeing up human employees for more strategic work.
- Cloud-Based Architecture: Many advanced ERP systems are cloud-based, offering greater scalability, flexibility, and accessibility.
- Real-Time Analytics: Advanced ERP provides real-time dashboards and analytics, enabling businesses to monitor performance and make data-driven decisions.
- Enhanced Customization and Integration: Advanced ERP systems offer greater flexibility in terms of customization and integration with other business systems.
The Importance of Business Process Automation
Automation is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity for businesses that want to thrive in the digital age. Here’s why business process automation through advanced ERP is crucial:
- Increased Efficiency: Automation eliminates manual tasks, reduces errors, and speeds up processes, leading to significant efficiency gains.
- Reduced Costs: By automating tasks and reducing errors, businesses can significantly reduce operational costs.
- Improved Accuracy: Automated processes are less prone to human error, leading to more accurate data and better decision-making.
- Enhanced Productivity: Automation frees up employees to focus on more strategic and creative tasks, boosting overall productivity.
- Better Customer Experience: Automation can improve customer service by providing faster response times and personalized experiences.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Advanced ERP provides real-time data and analytics, enabling businesses to make informed decisions based on facts, not gut feelings.
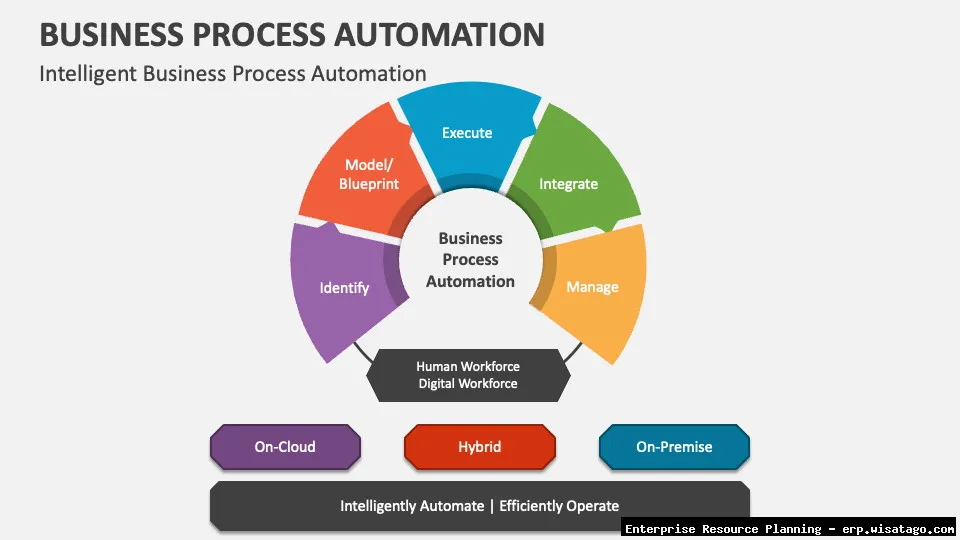
Core Features of Advanced ERP for Automation
Advanced ERP systems offer a wide range of features designed to automate various business processes. Understanding these features is crucial for selecting the right ERP solution for your organization.
Automated Financial Management
Financial management is a core function of any ERP system. Advanced ERP automates key financial processes, such as:
- Accounts Payable (AP): Automating invoice processing, payment scheduling, and reconciliation.
- Accounts Receivable (AR): Automating invoice generation, payment collection, and credit management.
- General Ledger (GL): Automating journal entries, financial reporting, and consolidation.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Automating budget creation, variance analysis, and financial forecasting.
Automated Supply Chain Management
Advanced ERP can significantly optimize your supply chain by automating processes such as:

- Demand Forecasting: Using AI and ML to predict future demand and optimize inventory levels.
- Inventory Management: Automating inventory tracking, replenishment, and optimization.
- Procurement: Automating purchase order creation, vendor management, and contract negotiation.
- Warehouse Management: Automating warehouse operations, such as receiving, putaway, picking, and shipping.
Automated Manufacturing Processes
For manufacturing companies, advanced ERP offers a range of automation capabilities, including:
- Production Planning: Automating production scheduling, capacity planning, and material requirements planning (MRP).
- Shop Floor Control: Automating data collection, process monitoring, and quality control on the shop floor.
- Bill of Materials (BOM) Management: Automating BOM creation, revision control, and cost tracking.
- Maintenance Management: Automating maintenance scheduling, work order management, and asset tracking.
Automated Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Integrating CRM with advanced ERP enables businesses to automate customer-facing processes, such as:
- Sales Force Automation: Automating lead management, opportunity tracking, and sales forecasting.
- Marketing Automation: Automating email marketing, social media marketing, and campaign management.
- Customer Service Automation: Automating ticket management, knowledge base management, and chatbot integration.
Automated Human Resources Management (HRM)
Advanced ERP can streamline HR processes by automating tasks such as:
- Recruitment and Onboarding: Automating job postings, applicant tracking, and employee onboarding.
- Payroll Processing: Automating payroll calculations, tax deductions, and payment processing.
- Benefits Administration: Automating benefits enrollment, eligibility verification, and claims processing.
- Performance Management: Automating performance reviews, goal setting, and employee development.
Implementing Advanced ERP: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing an advanced ERP system is a complex project that requires careful planning and execution. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the implementation process:
Step 1: Define Your Business Requirements
Before you start evaluating ERP vendors, it’s crucial to define your business requirements. This involves identifying your current pain points, defining your future goals, and documenting your specific needs for each department. A thorough requirements analysis will help you narrow down your options and select the ERP system that best fits your business.
Step 2: Evaluate ERP Vendors
Once you have a clear understanding of your requirements, you can begin evaluating ERP vendors. Consider factors such as:
- Functionality: Does the ERP system offer the features you need to automate your business processes?
- Scalability: Can the ERP system scale to accommodate your future growth?
- Cost: What is the total cost of ownership (TCO), including software licenses, implementation services, and ongoing maintenance?
- Vendor Reputation: What is the vendor’s track record in implementing ERP systems for companies in your industry?
- Customer Support: Does the vendor offer reliable customer support and training?
Step 3: Develop an Implementation Plan
A well-defined implementation plan is essential for a successful ERP implementation. Your plan should include:

- Project Scope: Clearly define the scope of the implementation project.
- Timeline: Establish a realistic timeline for each phase of the implementation.
- Budget: Allocate a budget for the implementation project, including software licenses, implementation services, and internal resources.
- Resource Allocation: Assign roles and responsibilities to team members.
- Data Migration Strategy: Develop a plan for migrating data from your legacy systems to the new ERP system.
- Training Plan: Develop a training plan to ensure that all users are properly trained on the new ERP system.
Step 4: Data Migration and Cleansing
Data migration is one of the most critical aspects of ERP implementation. It’s essential to cleanse and validate your data before migrating it to the new system. This will ensure that your data is accurate and consistent.
Step 5: Testing and Training
Before you go live with the new ERP system, it’s crucial to conduct thorough testing to ensure that all processes are working correctly. You should also provide comprehensive training to all users to ensure that they are comfortable using the new system. Modern businesses often seek ways to streamline operations, and ERP can be a key component in achieving that goal
.
Step 6: Go-Live and Post-Implementation Support
Once you’ve completed testing and training, you can go live with the new ERP system. It’s important to provide ongoing support to users after the go-live to address any issues that may arise. You should also monitor the performance of the ERP system and make adjustments as needed.
Common Pain Points and How to Overcome Them
Implementing an advanced ERP system can be challenging. Here are some common pain points and how to overcome them:
Resistance to Change
Employees may resist the new ERP system if they are not properly trained or if they perceive it as a threat to their jobs. To overcome this resistance, it’s important to communicate the benefits of the new system and involve employees in the implementation process.
Data Migration Challenges
Data migration can be a complex and time-consuming process. To avoid data migration issues, it’s important to cleanse and validate your data before migrating it to the new system.
Lack of User Adoption
If users are not properly trained or if they don’t see the value of the new ERP system, they may not adopt it. To ensure user adoption, it’s important to provide comprehensive training and demonstrate the benefits of the new system.

Cost Overruns
ERP implementations can be expensive. To avoid cost overruns, it’s important to develop a realistic budget and carefully manage your expenses.
Integration Issues
Integrating the new ERP system with other business systems can be challenging. To avoid integration issues, it’s important to carefully plan the integration process and test the integration thoroughly.
Choosing the Right Advanced ERP Solution
Selecting the right ERP solution is crucial for achieving your business goals. Here are some factors to consider when choosing an ERP system:
Industry-Specific Functionality
Choose an ERP system that offers industry-specific functionality. This will ensure that the system meets your specific needs and requirements.
Scalability and Flexibility
Choose an ERP system that can scale to accommodate your future growth and that offers the flexibility to adapt to changing business needs.
Cloud vs. On-Premise
Consider whether you want a cloud-based or on-premise ERP system. Cloud-based ERP systems offer greater scalability, flexibility, and accessibility, while on-premise ERP systems offer greater control and security.
Integration Capabilities
Choose an ERP system that can integrate with your other business systems, such as CRM, e-commerce, and supply chain management systems.
Vendor Reputation and Support
Choose a vendor with a strong reputation and a proven track record of successful ERP implementations. Also, make sure the vendor offers reliable customer support and training.
Conclusion
Business process automation through advanced ERP is a powerful tool for improving efficiency, reducing costs, and driving growth. By understanding the core features of advanced ERP, implementing a well-defined plan, and overcoming common pain points, businesses can successfully implement advanced ERP and achieve lasting success. Remember to prioritize a thorough needs assessment, careful vendor selection, and robust training to maximize your return on investment. The right ERP system, implemented correctly, can truly transform your organization and position you for success in today’s competitive marketplace.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this article has demonstrated the profound impact that Business Process Automation (BPA) facilitated by advanced ERP systems can have on organizations. By streamlining operations, reducing manual errors, and enhancing data visibility, BPA through ERP empowers businesses to achieve significant gains in efficiency, productivity, and profitability. The integration of technologies like AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation within ERP platforms is no longer a futuristic concept, but a present-day reality driving competitive advantage for those who embrace it.
The journey towards automating business processes through ERP requires careful planning, strategic implementation, and a commitment to continuous improvement. As businesses navigate the complexities of the modern landscape, the ability to adapt and optimize operations is paramount. We encourage you to explore the possibilities of advanced ERP solutions and consider how BPA can transform your organization. Contact us today to learn more about how our expert team can help you implement a tailored ERP solution to unlock your business’s full potential or visit our resources page at www.example.com/resources for further information.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Business Process Automation through Advanced ERP
How can implementing an advanced ERP system with automation capabilities improve operational efficiency and reduce manual data entry errors in my business?
Implementing an advanced ERP system with business process automation (BPA) capabilities significantly enhances operational efficiency by streamlining workflows and eliminating redundant tasks. By automating tasks such as invoice processing, order fulfillment, and inventory management, businesses can free up employees to focus on higher-value activities. Furthermore, automation reduces the likelihood of human error associated with manual data entry, leading to improved data accuracy and reduced costs related to correcting errors. Modern ERP systems often include features like robotic process automation (RPA) and artificial intelligence (AI) to further optimize processes. According to a recent study by McKinsey, companies that successfully implement automation in their business processes can see a 20-30% reduction in operating costs.
What are the key factors to consider when selecting an advanced ERP system for business process automation, particularly when integrating with existing legacy systems?
Selecting the right advanced ERP system for business process automation requires careful consideration of several factors, especially when integrating with existing legacy systems. Key factors include: (1) Compatibility: Ensuring the new ERP system is compatible with your current infrastructure and legacy systems is crucial. Look for systems that offer robust integration capabilities, such as APIs and pre-built connectors. (2) Scalability: Choose an ERP system that can scale with your business growth and changing needs. (3) Customization: Assess whether the ERP system offers sufficient customization options to adapt to your specific business processes. (4) Vendor Reputation: Research the vendor’s experience, customer reviews, and support services. (5) Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not only the initial purchase price but also implementation costs, training expenses, and ongoing maintenance fees. (6) Security: Ensure the ERP system has robust security features to protect sensitive data.
What are some common challenges businesses face when implementing business process automation through advanced ERP, and how can these challenges be effectively addressed?
Implementing business process automation through an advanced ERP system can present several challenges. One common challenge is resistance to change from employees who are accustomed to existing processes. Addressing this requires proactive change management, including clear communication, training, and involvement of employees in the implementation process. Another challenge is data migration, which can be complex and time-consuming. Proper data cleansing and validation are essential to ensure data accuracy in the new system. Integration issues with existing systems can also arise. A thorough assessment of integration requirements and a well-defined integration strategy are crucial. Finally, lack of adequate training can hinder user adoption and system effectiveness. Investing in comprehensive training programs for all users is essential. According to Gartner, organizations that invest in change management and training during ERP implementations are more likely to achieve successful outcomes.
